Report: Human Error Is the Leading Cause of Cloud Data Breaches
The human factor is still one of the biggest threats to cloud security, despite all the technology bells and whistles and alerts and services out there, from multi-factor authentication, to social engineering training, to enterprise-wide integrated cybersecurity platforms, and more.
That's a conclusion of the 2024 Thales Cloud Security Study, a new report from IT services and consulting company Thales based on a global survey of 2,961 respondents that was fielded in November and December 2023 via web survey with targeted populations for each country, aimed at professionals in security and IT management.
The issue is well known on organizational help desks where troubleshooters have long complained of the PEBKAC problem (Problem Exists Between Keyboard and Chair). But it's also a problem in the cloud, where human errors that have plagued IT for decades are still causing breaches that show little sign of slowing down.
"Human action can compromise security," the report noted. "Fueling this concern is the high number of cloud data breaches, with 44% of respondents reporting such an incident. Fourteen percent reported a breach in the past 12 months. Human error, issues with vulnerability and configuration management, and failures to use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) are all cited as leading contributors."
"Identity and Access Management (IAM) is crucial in linking people with technology and policy control," Thales added in a June 26 guest blog post on the site of the Cloud Security Alliance. "People's interaction with technology introduces significant risks, and human error is a leading cause of cloud data breaches."
Noting that almost half of organizations have experienced a cloud data breach, Thales said 31% attributed the breach to misconfiguration or human error, which the company said underscores the need for robust IAM solutions and comprehensive training to mitigate human-related risks. Following misconfiguration/human error, other concerns include vulnerability exploits or failure to implement controls on highly privileged access such as multi-factor authentication (MFA).
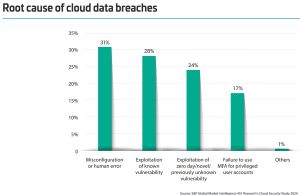 [Click on image for larger view.] Causes of Breaches (source: Thales).
[Click on image for larger view.] Causes of Breaches (source: Thales).
"The impact of human interaction is evident in the types of threats respondents are most concerned about," the report said. "While external attackers and malicious insiders ranked highly, human error — evident in incidents such as unintended actions — was often ranked number one."
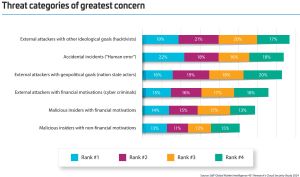 [Click on image for larger view.] Threat Categories (source: Thales).
[Click on image for larger view.] Threat Categories (source: Thales).
As the company's companion 2024 Data Threat Report indicates, the human problem hasn't changed much over the years, nor have attack types (report is from March 2024, data is from S&P Global Market Intelligence's 2021-2024 Data Threat custom surveys):
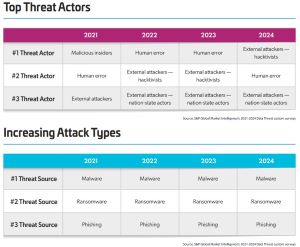 [Click on image for larger view.] Threat Actors/Attack Types (source: Thales).
[Click on image for larger view.] Threat Actors/Attack Types (source: Thales).